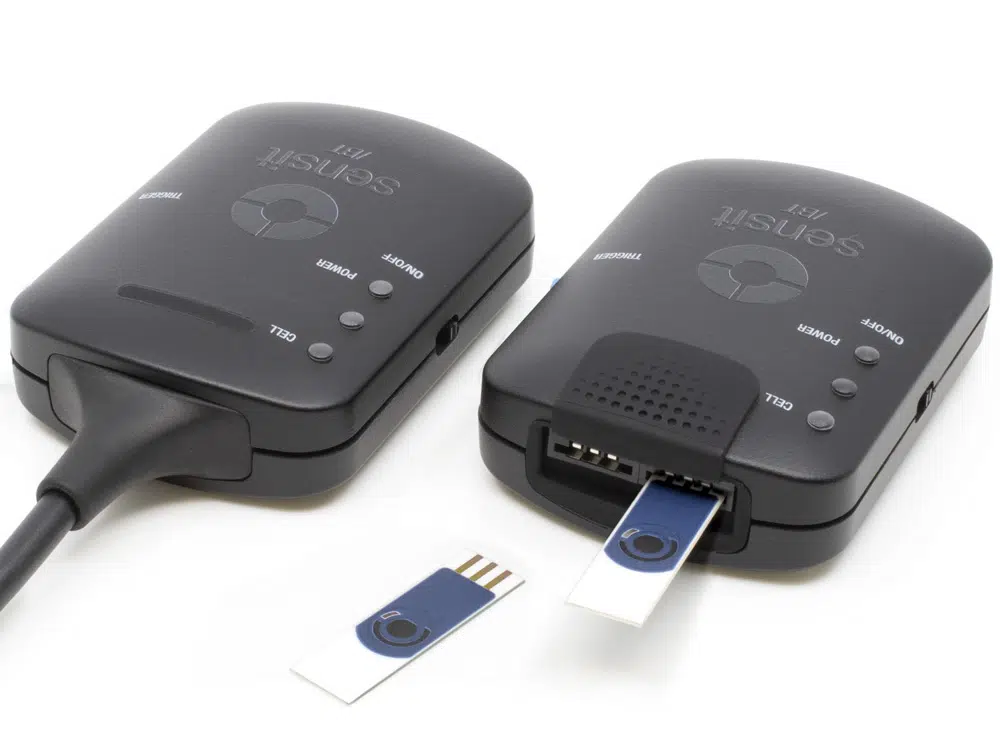
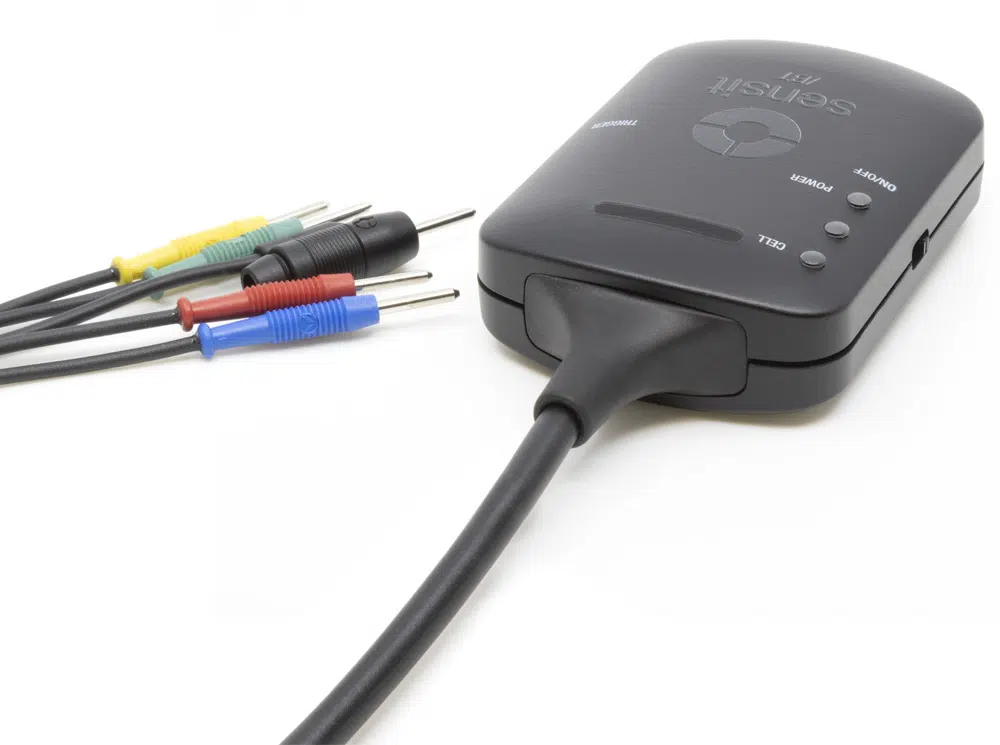
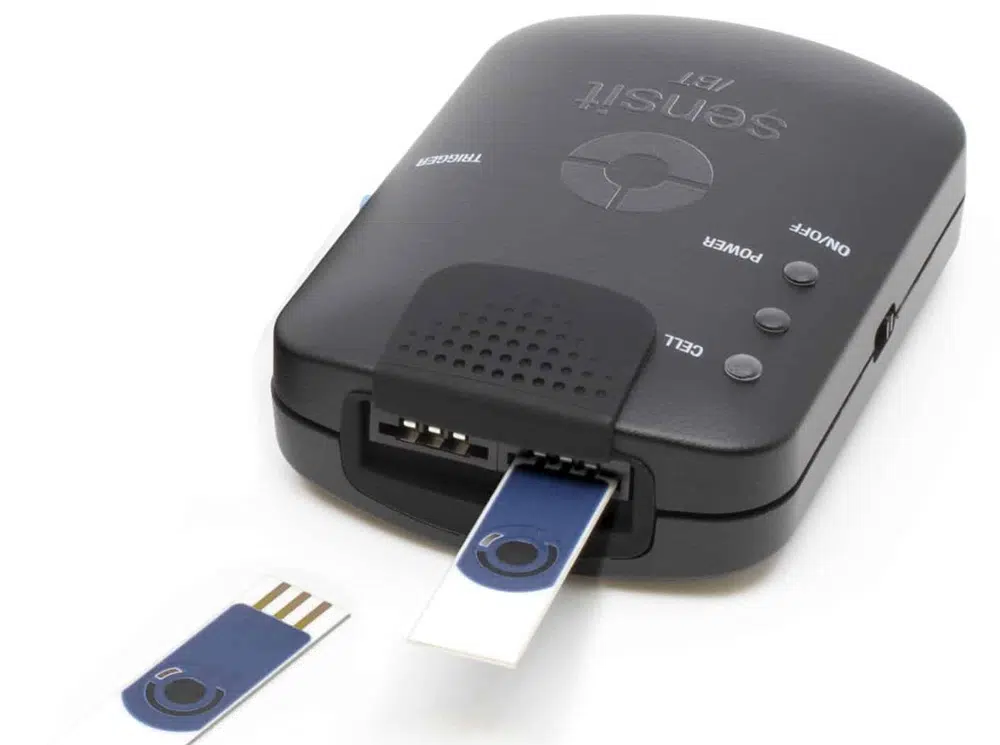
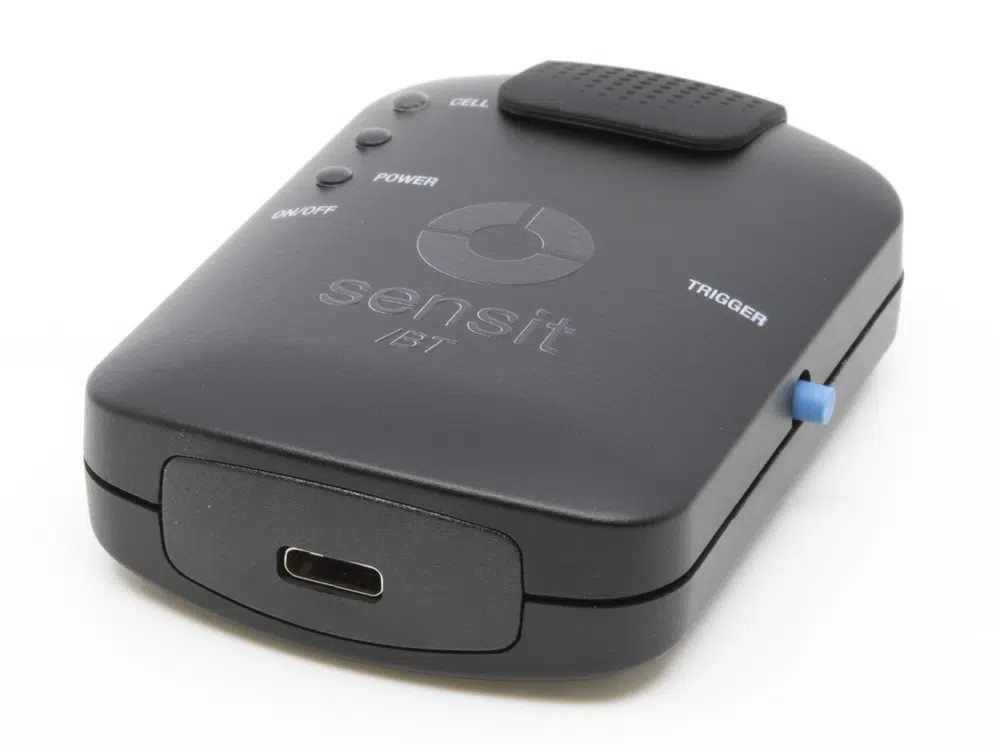
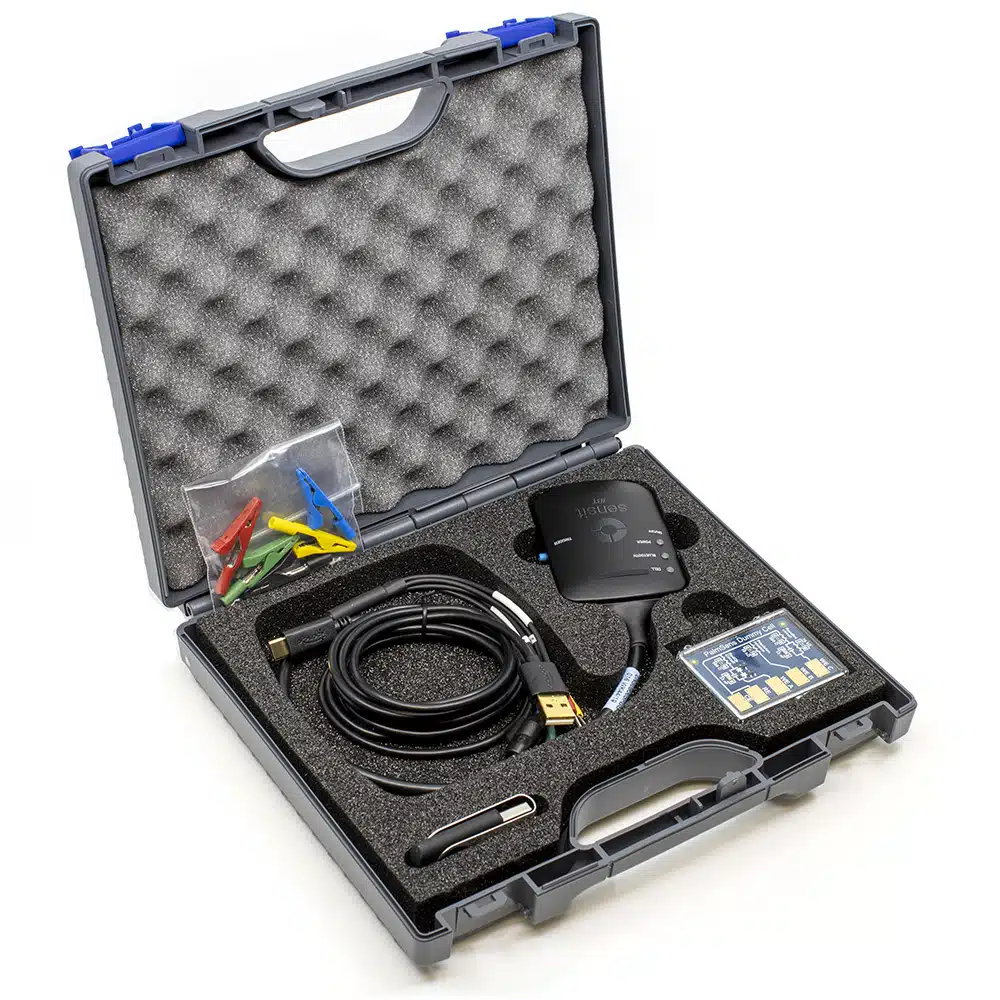
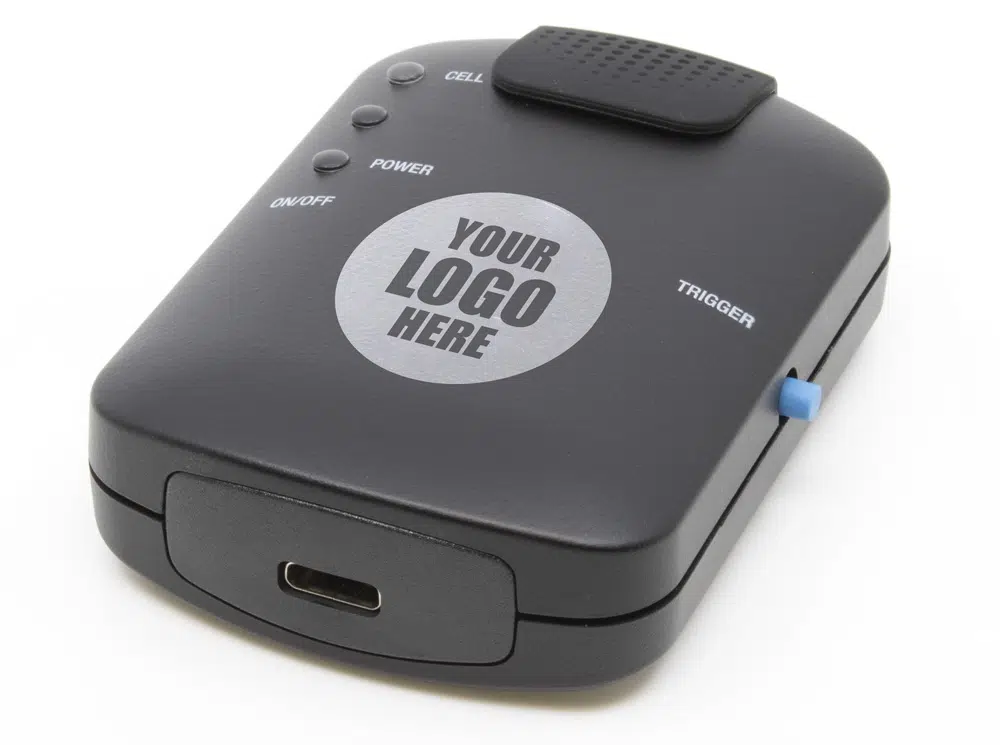
Sensit BT
Handheld and wireless dual-channel potentiostat
- Capable of EIS up to 200 kHz
- Built around the EmStat Pico module
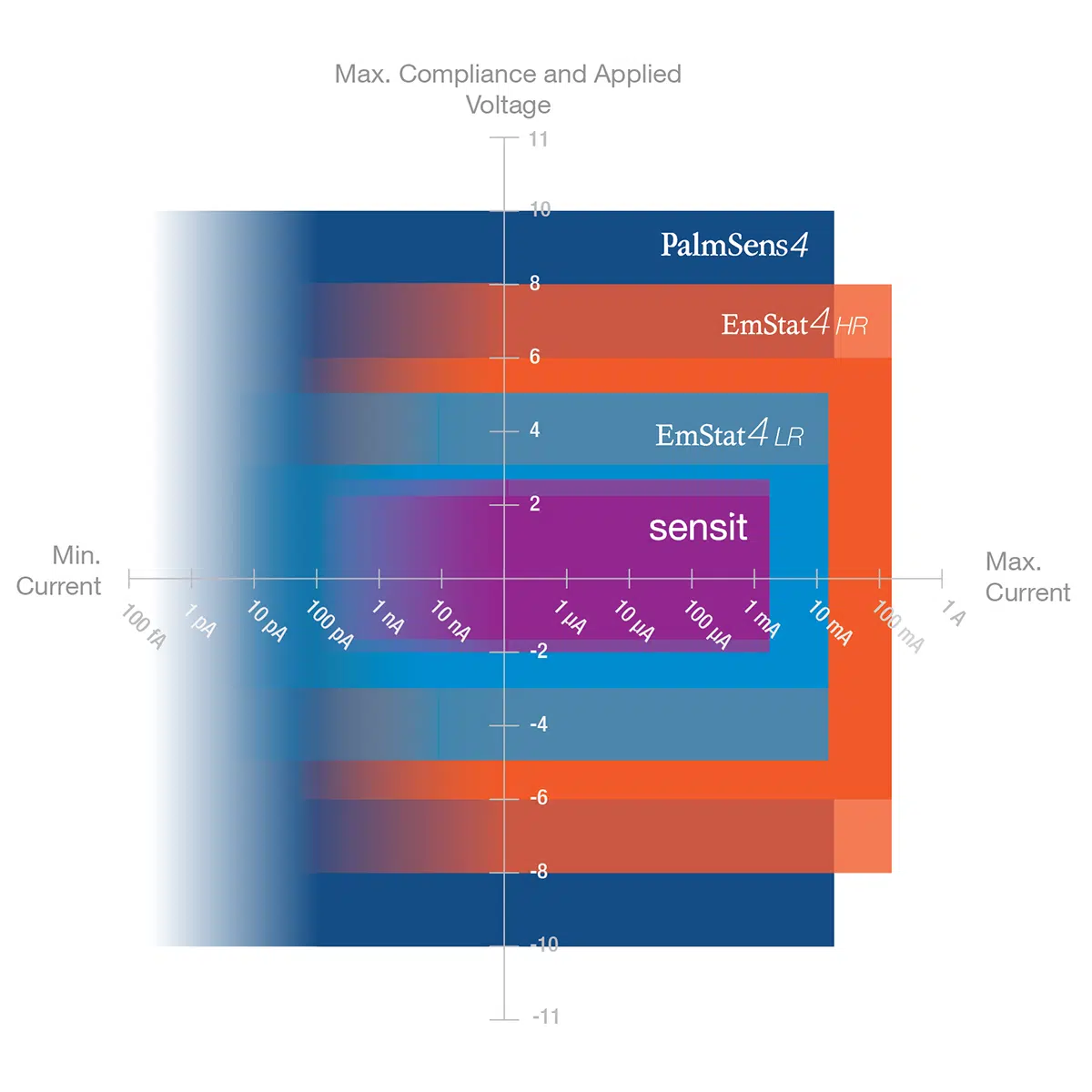
- Potential range -1.7 to +2 V
- Current ranges 100 nA – 5 mA (max ±3 mA)
- Can be used without PC or smartphone connection
Description
The Sensit BT is ideal for electrochemical sensor applications. The Sensit BT connects wirelessly to your smartphone or tablet and controlled via the Android app PStouch. You can use the USB-C port to charge the Sensit BT or connect to a classic USB port on your PC and control the Sensit BT via our PC software PSTrace.
The Sensit BT supports most common electrochemical techniques, including Cyclic Voltammetry, Square Wave Voltammetry and Impedance Spectroscopy (FRA/EIS).
Two versions:
|
Sensit BT.SPE |
Sensit BT.SNS |
||
|
|
|
||
| Sensor pitch | 2.54 mm | Cable length | 40 cm |
| Electrode connections | RE, WE, CE | Connectors | 2 mm banana |
| Allowed sensor thickness | Between 0.1 mm and 0.8 mm | Electrode connections | RE, WE, WE2, CE |
| Maximum sensor width | 11 mm | ||
Dual-channel and Bipotentiostat
The Sensit BT.SPE can be used for running sequential measurements on two different Screen-Printed Electrodes (SPE’s) each with their own Reference, Counter and Working electrodes.
The second channel can also be used in Bipotentiostat mode, functioning as second Working Electrode versus the Reference and Counter electrode of channel 1. Both working electrodes are recorded simultaneously in the Bipotentiostat mode.
The Sensit BT.SNS has a lead connected to the WE of channel 2 and can be used out-of-the-box for BiPotentiostat measurements.
On-board data storage
The Sensit BT is equipped with 500 MB internal storage memory.
Save measurements on-board as a backup. Or pre-program the device with a script and use the trigger button to run and store measurements: no need to connect a PC or smartphone. Browse and transfer all internally stored measurements back to the PC easily using PSTrace for Windows.
Specifications
| General | |
|---|---|
| Full dc-potential range
The maximum potential difference, that can be applied between WE and RE.
|
-1.7 to +2 V |
| Dynamic dc-potential range [1]
The maximum potential difference, that can be applied between WE and RE.
|
2.2 V |
Compliance voltage
The compliance voltage is the maximum voltage that can be applied between the working and counter electrode. Another name could be the maximum cell potential. Continue reading
|
-2.0 to +2.3 V [2] |
| Maximum current | ± 3 mA |
Max. data acquisition rate (datapoints / s)
Also known as Sampling Rate, it describes how fast the instrument can collect measurement values. Continue reading
|
1000 |
| Supports FRA/EIS |
Yes |
|
[1] The dynamic range is the range that can be covered during a single scan within the full potential range. For example; a linear scan can start at -1.5 V and end at 1.1 V or vice versa, covering 2.6 V dynamic range. [2] The compliance voltage is the maximum potential between Working and Counter electrode and depends on the selected mode. |
|
| Dual-channel and Bipotentiostat functionality |
|---|
|
| Potentiostat (controlled potential mode) | |
|---|---|
| Channels |
BT.SPE: 2 channels both with WE, RE and CE |
Applied dc-potential resolution
The lowest observable difference between two values that a measurement device can differentiate between.
|
537 µV |
Applied potential accuracy
The applied potential accuracy describes how close to the real values your applied potential is.
|
< 0.2% |
Current ranges
A current range defines the maximum current a potentiostat can measure in a certain range. Continue reading
|
100 nA to 5 mA (10 or 12 ranges, depending on the mode) |
| Current resolution | 0.006% of selected current range (5.5 pA on 100 nA range) |
Current accuracy
The current accuracy describes how close to the real values your measured current is. Continue reading
|
< 0.5 % of the current ±0.1% of range |
| Measured potential resolution (for OCP) | 56 uV (for OCP) |
| FRA / EIS (impedance measurements) | |
|---|---|
| Frequency range | 0.016 Hz to 200 kHz |
| Ac-amplitude range | 1 mV to 0.25 V rms, or 0.708 V p-p |
| Electrometer | |
|---|---|
Electrometer amplifier input
The amplifier input resistance of the amplifier in the electrometer determines the load that the amplifier places on the source of the signal being fed into it. Ideally the resistance is infinite, and the load to be zero to not to influence your measurement.
|
> 1 TΩ // 10 pF |
Bandwidth
Bandwidth defines the range of frequencies a system can accurately measure or respond to. Continue reading
|
250 kHz |
| Other specifications | |
|---|---|
| Power | USB / battery |
| Communication | USB (type C) and Wireless |
| Dimensions | 75 x 55 x 23 mm (excl. optional cable) |
| Weight | 75 g |
| Battery life | 12 hours at max. power consumption Full charge in < 3 hours |
| Auxiliary port | No |
| Storage memory | 500 MB for storing up to 16 million datapoints |
| EIS Accuracy Contour Plot |
|---|
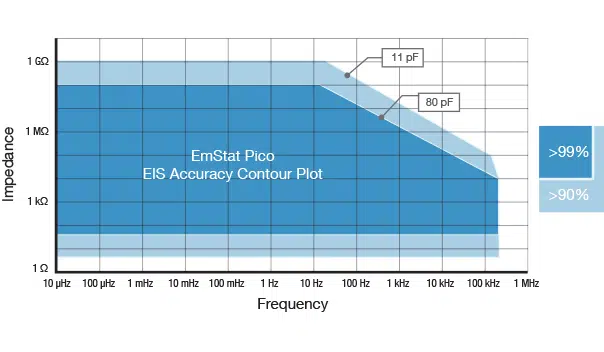 |
Software
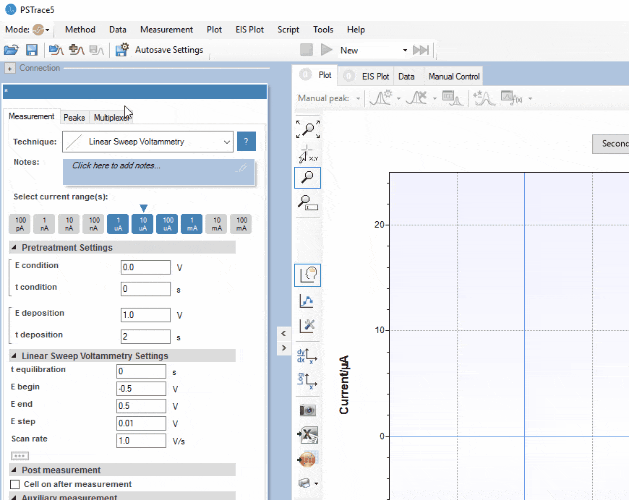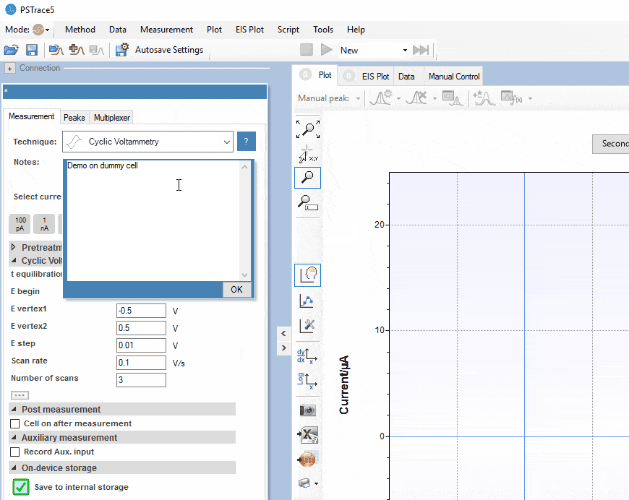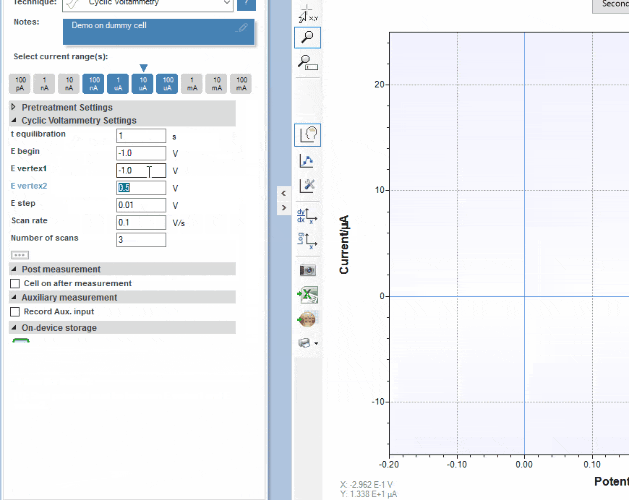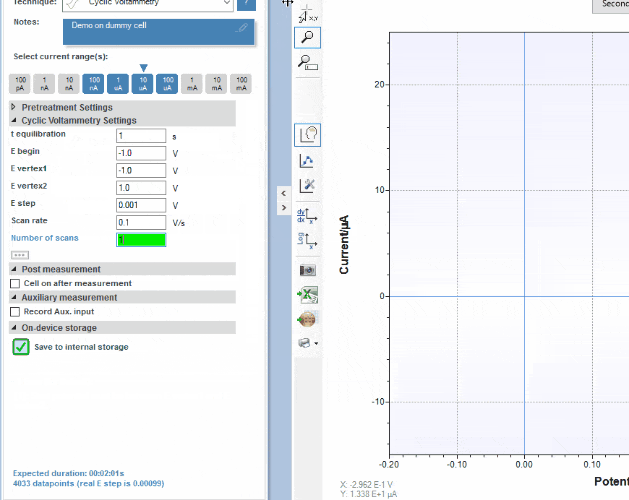
PSTrace
PSTrace is designed to be productive immediately after installation, without going through a long learning period. It has three modes; the Scientific mode which allows you to run all the techniques our instruments have to offer, and two dedicated modes for Corrosion analysis and the Analytical Mode. PSTrace is suitable for all levels of user experience.
Features include:
- Direct validation of method parameters
- Automated peak search
- Equivalent Circuit Fitting
- Scripting for running an automated sequence of measurements
- Open data in Origin and Excel with one click of a button
- Load data from the instrument’s internal storage
- and many more…
PStouch
PStouch is an app for Android devices compatible with all PalmSens, EmStat and Sensit potentiostats. The app connects to your potentiostat via USB (depending on the Android device) or via Bluetooth.
PStouch features include:
- Setting up and running measurements
- All files compatible with PSTrace
- Analysing and manipulating peaks
- Sharing data directly via email, Dropbox, or any other file sharing service
Get it on MyPalmSens
Software Development Kits
PalmSens provides several Software Development Kits (SDKs) to help developers create custom software to control their potentiostat. Each SDK comes with documentation and examples that shows how to use the libraries.
SDKs are available for:
- .NET (WinForms, WPF and Xamarin for Android)
- Python
- LabVIEW
- Matlab

MethodSCRIPT™ Communications Protocol
The Sensit-series work with MethodSCRIPT™, giving you full control over your potentiostat channels. The simple script language is parsed on-board, which means no DLLs or other type of code libraries are required. MethodSCRIPT™ allows for running all supported electrochemical techniques, making it easy to combine different measurements and other tasks.
MethodSCRIPT can be generated, edited, and executed in PSTrace.
MethodSCRIPT features includes:
- (Nested) loops and conditional logic support
- User code during a measurement iteration
- Exact timing control
- Simple math operations on variables (add, sub, mul, div)
- Data smoothing and peak detection
- Digital I/O, for example for waiting for an external trigger
- Logging results to internal storage or external SD card
- Reading auxiliary values like pH or temperature
- and many more…

Compatibility
My sensor fits the connector.
The required electrochemical technique for my application is supported.
The analyte conductivity does not require a compliance voltage of 2/2.3 V.
Downloads
Documentation (7)
| Name | Last updated | |
|---|---|---|
| MethodSCRIPT v1.7 The MethodSCRIPT scripting language is designed to improve the flexibility of the PalmSens potentiostat and galvanostat devices for OEM users. It allows users to start measurements with arguments that are similar to the arguments in PSTrace. PalmSens provides libraries and examples for handling low level communication and generating scripts for MethodSCRIPT devices such as the EmStat Pico and EmStat4. | 26-03-25 | |
| MethodSCRIPT v1.5 The MethodSCRIPT scripting language is designed to improve the flexibility of the PalmSens potentiostat and galvanostat devices for OEM users. It allows users to start measurements with arguments that are similar to the arguments in PSTrace. PalmSens provides libraries and examples for handling low level communication and generating scripts for MethodSCRIPT devices such as the EmStat Pico and EmStat4. | 25-03-24 | |
| Sensit BT Operator’s Manual Learn how to connect the instrument, understand the specifications, use the features and troubleshoot if needed. | 13-03-24 | |
| MethodSCRIPT v1.4 The MethodSCRIPT scripting language is designed to improve the flexibility of the PalmSens potentiostat and galvanostat devices for OEM users. It allows users to start measurements with arguments that are similar to the arguments in PSTrace. PalmSens provides libraries and examples for handling low level communication and generating scripts for MethodSCRIPT devices such as the EmStat Pico and EmStat4. | 01-02-23 | |
| Sensit BT Brochure Sensit BT Brochure | 09-09-22 | |
| MethodSCRIPT v1.2 MethodSCRIPT v1.2 protocol description | 28-04-20 | |
| MethodSCRIPT v1.1 MethodSCRIPT v1.1 protocol description | 17-04-20 |
Software (2)
| Name | Last updated | |
|---|---|---|
| PSTrace PC software for all single channel instruments PSTrace software is shipped as standard with all single channel and multiplexed instruments. The software provides support for all techniques and device functionalities. | 08-07-24 | |
|
MethodSCRIPT code examples
MethodSCRIPT code examples include:
- MethodSCRIPTExample_C - MethodSCRIPTExample_C_Linux - MethodSCRIPTExample_C# - MethodSCRIPTExample_Arduino - MethodSCRIPTExample_Python - MethodSCRIPTExample_iOS - MethodSCRIPTExample_Android Every code example comes with a "Getting Started" document. |
07-07-24 |
Application Note (3)
| Name | Last updated | |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C Detection with ItalSens IS-C This application note describes how to create a calibration for quantitative measurements of vitamin C. Due to the detailed description and harmless solutions this an excellent electrochemical experiment with liquids for beginners in the field of electrochemistry. | 27-01-21 | |
| Limitations for EIS on EmStat Pico | 18-12-20 | |
| Connect SensitBT using wireless communication This application note describes various ways to connect the portable SensitBT using wireless communication. To connect using Android you can use PSTouch, in Windows you can use PSTrace or MethodSCRIPT. In iOS you can use MethodSCRIPT. | 10-11-20 |